
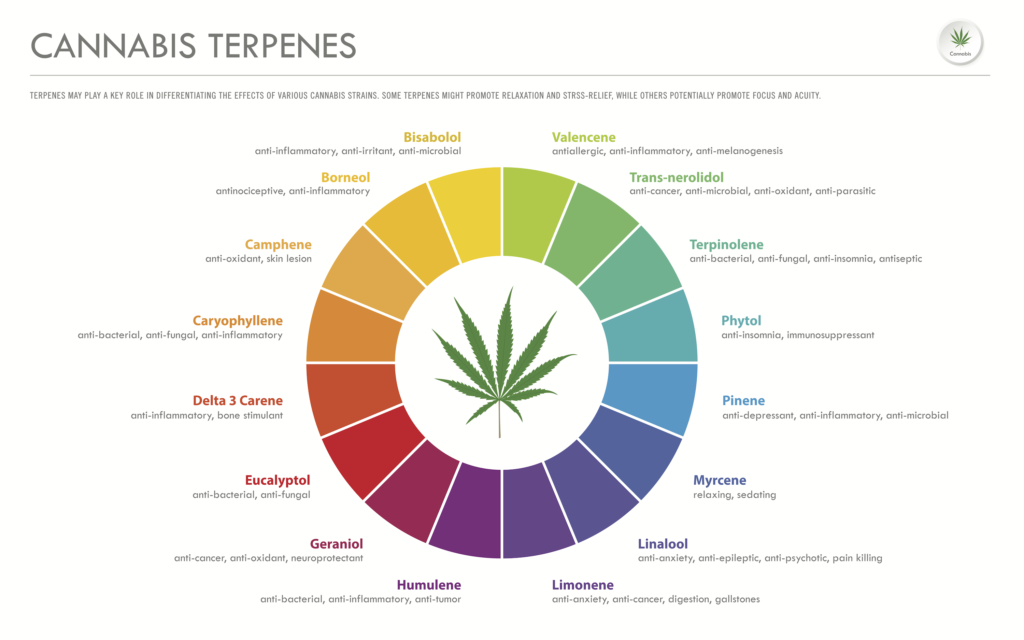
Terpenes are aromatic compounds that are found throughout nature. From fruits and vegetables to trees and cannabis, terpenes are everywhere. Not only do they play a major role in determining the scent and flavor of your cannabis, but they also impact the effects of each strain.
“The Entourage Effect” is a widely-held theory that describes how the terpene profile of each cannabis strain gives it unique effects. Many believe terpenes are why some strains may make you feel sleepy, while others make you feel quite productive and spry.
Uplifting terpenes that boost your energy are generally associated with “sativa” cannabis products. More relaxing, sleep-inducing terpenes are usually found in “indica” labeled products.
Knowing which terpenes work best for you can enhance your medical cannabis experience and help inform your purchasing decisions at dispensaries. If you’re looking for a strain that might put a little extra pep in your step, here are the terpenes you should keep an eye out for.
Terpenes That Support Energy and Focus — Limonene, Pinene, Terpinolene, and More
All terpenes have their own therapeutic effects that are complementary to those associated with phytocannabinoids. Such effects range from energizing to sedating and anti-inflammatory to antimicrobial.
Limonene, pinene, and terpinolene are terpenes that fall into the “energizing” category. They’re also typically associated with sativa or hybrid strains of cannabis.
Further Readings: Sativa vs Indica: What’s the Difference?
However, these terpenes aren’t just energizing — they have other beneficial properties, too.
Limonene — An Energizing Terpene with Neuroprotective and Antibacterial Effects

Found in citrus peels and the rinds of other tropical fruits, limonene is also one of the most common terpenes found in cannabis. Much like one might find an orange refreshing and uplifting, limonene is associated with having similar effects in cannabis.
Not only is it one of the best terpenes for productivity, but limonene is dually associated with the following therapeutic effects:
- Neuroprotective (helps prevent the damage, degeneration, and impairment of nerve cells): A 2021 Molecules journal review suggests limonene may help alleviate or protect against neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, and Multiple Sclerosis. The review also highlights evidence that limonene may aid in the treatment of migraines, epilepsy, and depression.
- Antibacterial and antimicrobial: Limonene has antibacterial and antimicrobial properties, making it a common staple in soaps and cleaning products.
- Potential anti-cancer & chemopreventive properties: In rodent models, limonene was shown to reduce breast tumors and protect against the development of secondary tumors. However, these same results have yet to be observed in human trials. More research is needed.
- Antioxidant: Limonene has antioxidant properties, which may protect your cells from damage caused by free radicals.
- Pain relief: Lastly, limonene displays anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties, according to a Pharmacological Reviews article.
α-Pinene and β-Pinene for Boosting Productivity

Pinenes are some of the most abundant terpenes in nature. They’re affiliated with the cozy scent of pine trees and the perfumey aroma of rosemary. Additionally, α-pinene and β-pinene are quite common in cannabis, particularly in sativa strains of cannabis.
Like limonene, the benefits of α-pinene and β-pinene extend beyond their ability to enhance your focus. Due to their similarities, there is some overlap between their effects. Studies on the therapeutic potential of α-pinene and β-pinene are summarized below.
α-Pinene (alpha pinene):
- Antibacterial: α-Pinene’s antibacterial properties were tested against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), which is notoriously difficult to treat due to its strong antibiotic resistance. α-Pinene was also tested against Escherichia coli (E. coli). α-Pinene exhibited antibacterial activity against both MRSA and E. coli.
- Antifungal: α-Pinene exhibits antifungal properties, especially against Candida species of fungi. Candida is a type of yeast that is known to infect humans.
- Anti-inflammatory: In multiple studies, α-pinene has displayed its ability to decrease inflammatory markers throughout the body.
- Gastroprotective: One study has shown α-pinene may prevent the development of gastric ulcers. However, more research is needed to further support these findings.
β-Pinene (beta pinene):
- Supports digestive health: In a study using essential oils from Eucalyptus tereticornis, the researchers found β-pinene and α-pinene effective in enhancing gastric tone, relaxing the duodenum, and accelerating the gastric emptying of liquids. For context, gastric tone refers to the stomach’s sensitivity to distension — i.e., bloating. The duodenum is the first portion of the small intestine, and it is connected to the stomach. The duodenum serves as the “mixing area” for partially digested foods, bile from the liver, and pancreatic juices.
- Antibacterial and Antifungal: Studies on β-pinene have found it effective against several strains of bacteria and multiple species of Candida fungi.
- Anticonvulsant: α-Pinene and β-pinene both reduced seizure intensity in rodent models of epilepsy.
Terpinolene — The Terpene for Mental Clarity

Terpinolene is a floral terpene found in apples, cumin, tea trees, lilacs, and of course, cannabis.
“While claimed to be sedative, terpinolene is strongly associated with cognitive clarity and ‘sativas,’” explains author Michael Backes in his book, Cannabis Pharmacy: The Practical Guide to Medical Marijuana. “Terpinolene is the stimulating terpene associated with early citrus Thai landraces.”
In addition to being stimulating and revitalizing, terpinolene is associated with the following therapeutic effects:
- Antifungal: Repeatedly, studies have shown terpinolene effective against several species of fungi, including those of the Candida genus.
- Antibacterial: Terpinolene displays antibacterial effects against S. aureus, E. coli, and other strains of bacteria.
- Antiviral: Several studies have proposed terpinolene may be effective against Influenza A virus, Herpes simplex virus type 1, and Poliovirus 1.
- Antioxidant: Many studies have consistently found that terpinolene has strong antioxidant properties.
- Insecticide: Terpinolene displays natural insecticidal properties against insects, larvae, and mites.
Key Takeaways: Terpenes Could Boost Your Energy & Focus
Every strain of cannabis is a little different. While some may lull you into a five-hour nap in the middle of the day, others might have you rejuvenated and ready to conquer the rest of your to-do list.
This wide variation between strains is largely due to the Entourage Effect, which is a theory that describes the synergy between phytocannabinoids and terpenes. In other words, each strain’s cannabinoid and terpene profiles give it unique properties.
Familiarizing yourself with the various types of terpenes and their effects will help you find edibles for focus and energy. If you’re looking for cannabis strains that will lift your mood, elevate your energy, and enhance your focus, keep an eye out for varieties high in limonene, α-pinene, β-pinene, and terpinolene.
References
- Eddin, L. B., Jha, N. K., Meeran, M. F. N., Kesari, K. K., Beiram, R., & Ojha, S. (2021). Neuroprotective Potential of Limonene and Limonene Containing Natural Products. Molecules, 26(15), 4535. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154535
- Chebet, J. J., Ehiri, J. E., McClelland, D. J., Taren, D., & Hakim, I. A. (2021). Effect of d-limonene and its derivatives on breast cancer in human trials: a scoping review and narrative synthesis. BMC Cancer, 21(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-021-08639-1
- Lobo, V., Phatak, A., & Chandra, N. (2010). Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health. Pharmacognosy. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-7847.70902
- Liktor-Busa, E., Keresztes, A., LaVigne, J., Streicher, J. M., & Largent-Milnes, T. M. (2021). Analgesic Potential of Terpenes Derived from Cannabis sativa. Pharmacological Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1124/pharmrev.120.000046
- Allenspach, M., & Steuer, C. (2021). α-Pinene: A never-ending story. Phytochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2021.112857
- Centers for Disease Prevention and Control. (2020, October 30). Candidiasis | Types of Diseases | Fungal Diseases | CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/diseases/candidiasis/index.html
- Salehi, B., Upadhyay, S., Orhan, I. E., Jugran, A. K., Jayaweera, S. L. D., Dias, D. A., Sharopov, F., Taheri, Y., Martins, N., Baghalpour, N., Cho, W. C., & Sharifi-Rad, J. (2019). Therapeutic Potential of α- and β-Pinene: A Miracle Gift of Nature. Biomolecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9110738
- Backes, M., & Md, W. A. (2017). Cannabis Pharmacy: The Practical Guide to Medical Marijuana (1st ed.). Black Dog & Leventhal.
- Menezes, I. O., Scherf, J. R., Martins, A. O., Ramos, A. G., Quintans, J. de, Coutinho, H. D., Ribeiro-Filho, J., & de Menezes, I. R. (2021). Biological properties of terpinolene evidenced by in silico, in vitro and in vivo studies: A systematic review. Phytomedicine, 93, 153768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153768