
When you enter a dispensary, you’ll notice the shelves are lined with brightly-colored labels to indicate whether a product is a “sativa,” “indica,” or “hybrid.” Each category offers you a different type of product experience, so how are you to know which is right for you?
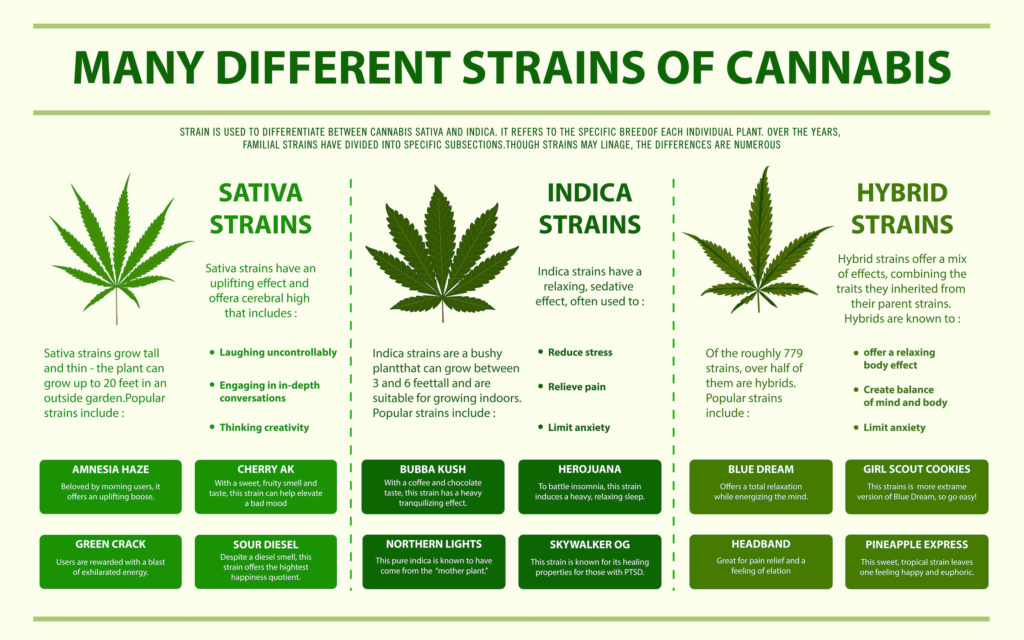
Generally speaking, sativa strains are regarded as more uplifting, invoking somewhat of a cannabis “buzz.” Indica strains tend to be more mellow and sedating, whereas hybrid varieties offer a mix of both sativa and indica effects.
However, there is more than meets the eye to the terms “sativa” and “indica.” While they are derived from the taxonomic names for different cannabis plant subspecies, it’s a common misconception that all strains labeled “sativa” are derived from Cannabis sativa and all strains labeled “indica” are derived from Cannabis indica.
Sativa and Indica: The Botanical Definitions
From a plant biology perspective, Cannabis is a genus that includes three species of wind-pollinated, annual-flowering plants indigenous to Asia.
If you’re unfamiliar with taxonomy, a genus is essentially the “generic” name while the species refers to a specific member of the genus. For example, Canis is a genus that includes various species, such as dogs, wolves, and coyotes. Dogs, wolves, and coyotes are entirely different from one another as individual species, yet they’re still related and grouped into the same category.
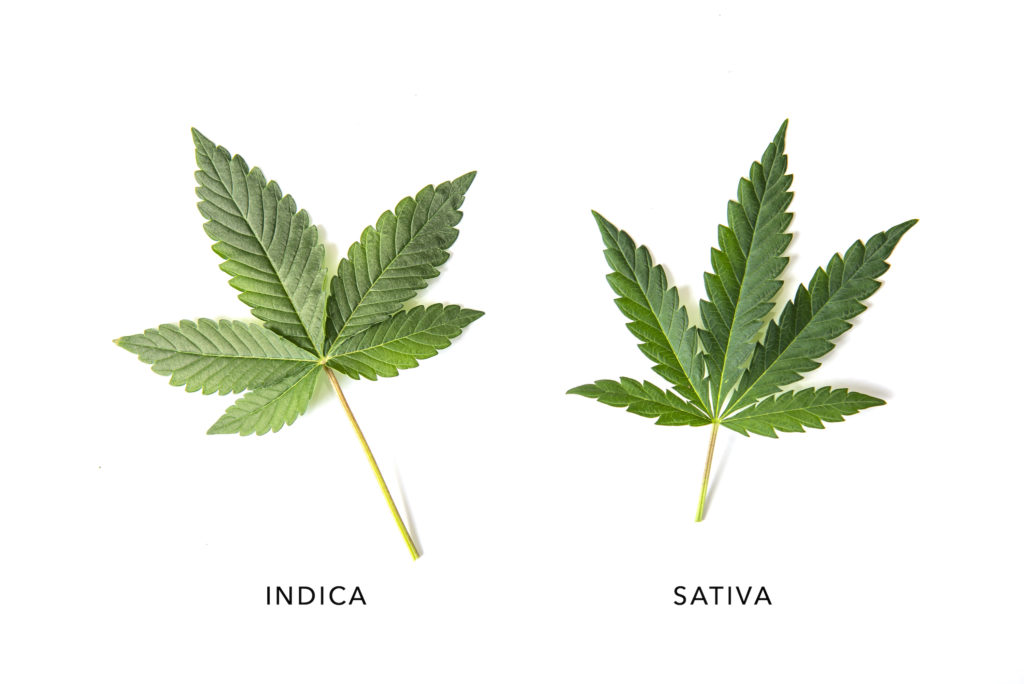
Cannabis sativa (C. sativa) is a species that can grow from five to 18 feet tall with sparse branches and thin leaves. It’s also the most common species of Cannabis in the western hemisphere.
Cannabis indica (C. indica) is a much shorter subspecies of C. sativa, only growing to about two to four feet tall. In contrast to C. sativa, C. indica plants are densely packed with branches, leaves, and flowers. Its leaves are also broader than that of C. sativa plants.
C. sativa and C. indica are not considered two separate species because they can be bred together. Instead, C. indica is regarded as a subspecies of C. sativa.
However, in the popular media and in day-to-day cannabis use, sativa and indica labels often have nothing to do with which plant subspecies the product was derived from.
Sativa and Indica: The Modern Definition
The legalization of cannabis from state to state has opened grounds for massive breeding and hybridization efforts. Often in the pursuit of growing the highest THC strains, growers have bred cannabis to a point where “sativa” and “indica” labeled products are genetically indistinct from one another.
Studies that have compared the differences between commercial cannabis to federally grown cannabis for research purposes also found no significant genetic correlations between products that were labeled “sativa,” “indica,” or “hybrid.”
Due to the breeding practices of the modern cannabis industry, the strains you purchase are rarely ever “100 percent C. sativa” or “100 percent C. indica.” In reality, the overwhelming majority of commercial cannabis products are hybrids. The sativa and indica labels are more or less marketing terms to communicate or advertise to consumers how a strain might make them feel.
If the strain offers more of a buzz, the grower will call it a sativa. Likewise, if the strain tends to lull you into a deep slumber, the grower will call it an indica.
Sativa v.s. Indica: Terpenes and The Entourage Effect

To break it down a bit further, “The Entourage Effect” is a prevailing and widely accepted theory about how terpenes may alter the way cannabinoids are processed and used throughout your body.
Terpenes are the compounds in cannabis plants that alter its scent and flavor. They are abundantly found throughout nature and food-bearing plants. Furthermore, terpenes are associated with their own therapeutic properties.
Thus, it’s widely believed the different properties of sativa and indica products are dictated by which terpenes they have.
For example, limonene is a terpene found in the rinds of citrus plants and other fruits. It is also one of the most common terpenes found in cannabis plants. Limonene is believed to have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, immune-modulatory, anticancer, and gastroprotective properties.
It’s also commonly regarded as an uplifting and energetic terpene, usually found in high quantities in sativa and hybrid cannabis products.
On the other end of the spectrum, myrcene is another very common terpene found in cannabis. Myrcene reportedly has anxiety-reducing, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-aging, and pain-relieving properties.
The terpene is found in particularly high quantities in indica labeled products, leaving many experts to believe myrcene is behind the infamous “couch-lock” effect of a strong indica.
Sativa v.s. Indica: Which is Right For You?
Familiarizing yourself with the terpenes associated with indica and sativa labeled products can better inform your purchasing decisions at dispensaries.
If you’re looking for a cannabis strain that might boost your mood, increase your focus, or motivate you to clean your entire house, opt for a sativa high in the terpenes limonene and pinene.
α-Pinene and β-pinene are found in a variety of plants — including cannabis. They appear to have antibiotic, antimicrobial, antitumor, and anti-inflammatory effects. Like limonene, α-Pinene and β-pinene are also associated with sativa strains.
But if you’re looking for a strain that’ll help you unwind after a long day at work and potentially improve your sleep, go for an indica high in myrcene and linalool terpenes. Linalool is a terpene found in lavender and cannabis plants that is known for its sedating, stress-relieving properties.
Key Takeaway: Utilizing Sativa and Indica Strains For Your Benefit

- Most commercially available cannabis products are not 100 percent C. sativa or C. indica. Rather, the plant they’re derived from is typically a hybrid stemming from a long line of C. sativa and C. indica plants that have been bred together.
- There are often no genetic correlations between cannabis products and their “sativa,” “indica,” or “hybrid” labels.
- In the modern cannabis industry, the terms “sativa” and “indica” are used to communicate how a product might make you feel.
- Terpenes play a major role in dictating how a cannabis strain will make you feel. This interaction between terpenes and cannabinoids is known as “The Entourage Effect.”
- Sativa strains are associated with uplifting, energizing, and focus-enhancing effects.
- Indica strains are associated with calming, sedating, and anxiety-relieving effects.
To dive deeper into the differences between sativa and indica, we recommend listening to episode five of the Cannabis Science Today podcast from the Agricultural Genetics Foundation.
In this episode, Cannabis Science Today host Emily Fata interviews Dr. Daniela Vergara, a cannabis geneticist from Cornell University who has done extensive research on cannabis and hops plants over the last few years. Together, they educate listeners on the important differences between sativa and indica.